We’ve enjoyed some return to normalcy after the intensity of the early COVID years. However, it’s important to remember that our young children are still living with some of the impacts of the changes we all experienced. One of the reasons the COVID years have affected our children is because so much critical development happens in the first few years of life.
While home is an incredibly nurturing place, many of our children were limited to only being at home which led to fewer opportunities for socializing and learning different kinds of relationship skills. To further complicate the scene, many of us were also trying to juggle our own changes in work and life.
With all this in mind, we’ve been focusing on identifying some impacts of COVID and sharing strategies to support optimal development in our young children.
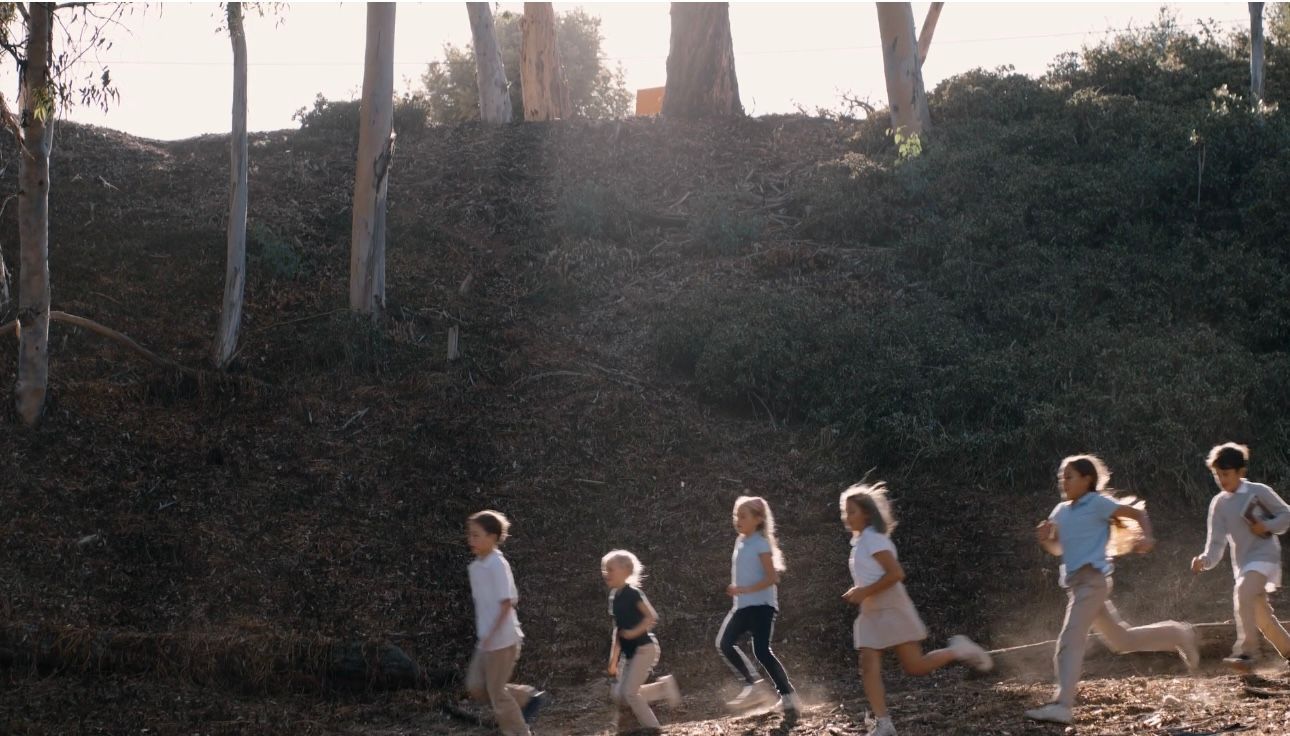
Socializing with Peers
During the early COVID years, children didn’t have as much time to be around others, especially other children. Even when we could be with other people, we all needed to maintain a physical distance.
Yet children learn how to navigate social situations through play. Think of the rough and tumble romping of wolf puppies. It is through those interactions that the pups strengthen social bonds and learn how to navigate social status in the pack. Similarly, during interactive play, children learn to negotiate, share, wait for a turn, follow the rules of a game, and consider others’ feelings.
Our children now have an intense hunger for socialization while their socialization skills are still developing.
To support their social development, we can:
- provide plenty of opportunities for unstructured imaginative play with peers
- observe to see if children are hanging back or avoiding interactions
- offer gentle help for joining into play or suggest phrases children can use to ask to participate
- recommend tasks they can do to help the group
- identify real-time emotions
- model positive communication
Before intervening, though, it’s also important to give time and space for children to negotiate and problem-solve. Children learn best through opportunities to make some mistakes and, just like with the wolf pups, the learning might look a little messy at first!
Connecting to the Real World
Many of our children have had a lot more screen time over the past few years. According to Carlota Nelson, director of the documentary Brain Matters, too much screen time can impact children’s concentration and focus, reduce their ability to control impulses, and affect their capacity for empathy.
Young children need lots of opportunities for concrete, tangible, hands-on play. They need to use their bodies and hands to manipulate the world around them. Plus, multi-sensory experiences help children develop strong neural pathways.
To help this real-world connection, we can:
- provide more time in nature and green spaces
- incorporate more movement, exercise, and free play into the day
- play board or card games with our children (or just play with them!)
- make sure to practice and model face-to-face interactions and eye contact
- engage in healthy human touch
- reduce passive screen time
As an added bonus, these pursuits also provide children with more opportunities to experience a language-rich environment. As we know, the amount and quality of language children experience have a direct correlation with the rate of their language development. Thus, they need plenty of experiences to develop their language skills through listening to and interacting with a variety of people around them.
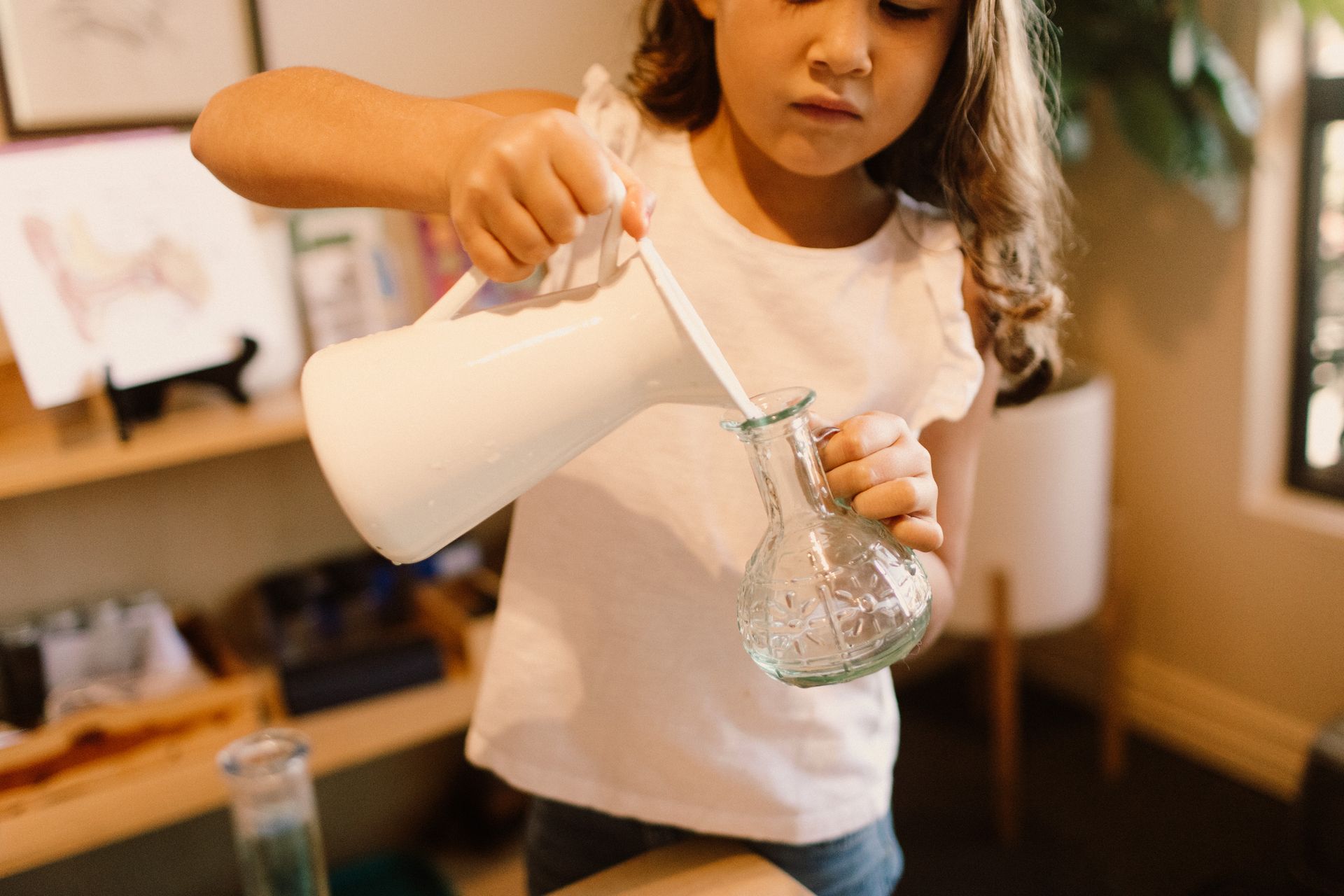
Developing Independence
Being home more with our children led to lovely family time, however it also may have increased our children’s reliance upon our presence while decreasing their tolerance for uncomfortable situations. Yet as children grow, they need opportunities to develop independence. These experiences are immensely important for children to build a sense of self while also increasing their self-esteem, frustration tolerance, and perseverance.
Rather than shield our children from challenging situations, we can make sure they have practice with experiences that can be a little anxiety-provoking. Anxiety is a normal human feeling and helps our bodies prepare us for something that might be hard. So our children can gain practice in how to regulate themselves, they need opportunities to be a bit out of their comfort zone.
To develop our children’s confidence, we can:
- expose our children to experiences that can produce a little healthy anxiety
- create opportunities for children to talk and share their thoughts
- engage in warm, responsive conversation (with lots of listening!)
- experience and discuss stories or situations together
- teach practical life skills for self-sufficiency
- include our children in household chores
As children become more confident, they are better able to handle transitions, experience less anxiety, and become more flexible. If you need any more convincing, Psychology Today references a study showing that children who started contributing to family chores at age three or four were more likely to have successful relationships, engage in rewarding careers, and be more self-sufficient in their lives.
As we shift into more regular routines after the intensity of the pandemic, let’s use this time to bring out the best in our children.
“We then become witnesses to the development of the human soul; the emergence of the New [Human], who will no longer be the victim of events but, thanks to his clarity of vision, will become able to direct and to mold the future of [human]kind.”
– Dr. Maria Montessori, The Absorbent Mind
We welcome you to visit the school to see firsthand how we support our future leaders, the young children, as they develop their independence, strengthen their social bonds, and make lasting connections with the wonder of the world.


